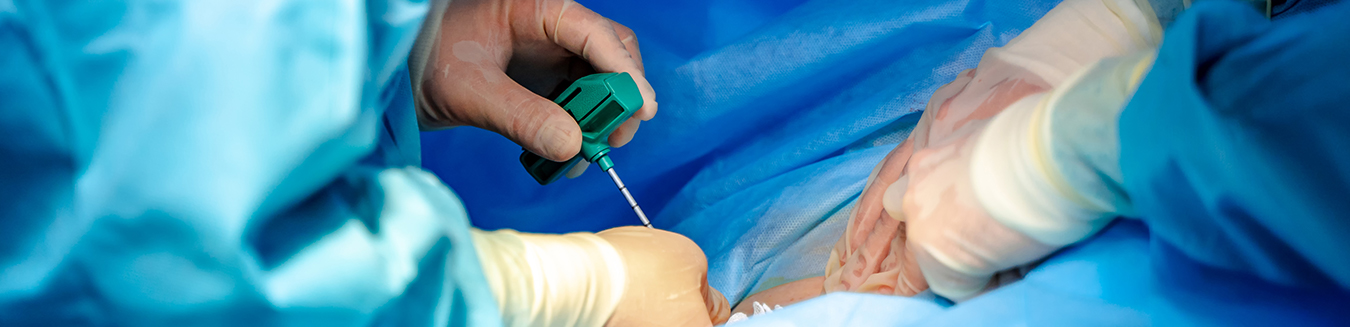
Bone marrow and stem cell transplantation replaces the bone marrow of a patient with new bone marrow that is taken from a donor or the patient himself.
How can one donate bone marrow?
The donor can donate his or her bone marrow under anesthesia using two methods:
- Medium-sized needles are used to collect bone marrow from the pelvic bones. This procedure usually takes one hour and involves the collection of about a quarter to half a liter of blood-like material.
- The donor is hooked up to a special machine resembling one used for dialysis. This machine selects stem cells (which comprise a very small fraction of circulating cells in the blood) and returns the rest to the donor. These stem cells may be used the same way that bone marrow is used. The BMT specialist will select the more suitable procedure.

What is an autologous transplant?
If bone marrow or stem cells are collected from the patient himself, then this is called autologous transplant or high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue. Usually this is done after having received chemotherapy. The collected cells are stored until large doses of chemotherapy are given to eradicate residual malignant cells. The stem cells are then injected to help bone marrow recovery. Autologous transplants are usually done for solid tumors like Ewing sarcoma or neuroblastoma.
What is an allogeneic transplant?
In allogenic transplants – also called a homeopath, genealogical or lineage implant – the bone marrow or stem cells are taken from a donor. Afterward, the collected cells are infused to the patient to replace their bone marrow. Allogeneic transplants are usually performed in cases of leukemia, where the new cells may attack any residual cancer cells. This transplant may also be carried out in cases of bone marrow failure or thalassemia.

Can anyone donate bone marrow?
To be eligible to donate, you have to be HLA-compatible. HLA are proteins that are located on the surface of white blood cells and other tissues in the body. HLA antigens are like blood types, wherein not all people can be blood donors for each blood type. Similarly, only compatible individuals can safely receive bone marrow . The chance of matching between siblings is about 25%.

How are bone marrow and stem cells infused?
The procedure is simple; it is similar to a regular blood transfusion and usually lasts for less than an hour. Nonetheless, doctors and nurses take this process very seriously, thoroughly identifying the unit of bone marrow to make sure it is the ordered unit. They also closely monitor the patient during infusion.

What is engraftment?
Engraftment is when the transplanted cells start to produce new cells in the bone marrow. At that time, your old blood cells are gone. Your cell numbers will recover in about 2 weeks, depending on the type of transplant. First the white blood cells come back, then the red blood cells. You may need months to be completely independent of platelet and blood transfusions. Full recovery of your immune system may take between 6-12 months.
The side effects of bone marrow transplantation
Immediate complications may occur, usually as a result of chemotherapy. This includes mouth ulcerations, nausea, vomiting and liver toxicity (depending on the level of liver damage). Blood stream infections are also very common, but are usually controlled with antibiotics until your blood cells recover. In an Allogeneic transplant, graft versus host disease is another potential complication. Below are some side effects of bone marrow transplantation.

Fatigue

Mouth sores

Bleeding gums, nosebleeds
or blood in your urine
Loss of appetite

Difficulty
eating or drinking

Diarrhea
Graft versus
host disease
What is graft versus host disease?
This is the most common complication from an allogeneic transplantation. It occurs when the transplanted white blood cells identify the body tissue (the host) as "foreign" and proceed to attack them. It starts with a skin rash, mild liver problems, and diarrhea that can be severe. This may be controlled with extra medications, including corticosteroids. The process may be prolonged and difficult to control, and can ultimately affect any organ.